periventricular white matter
There is some involvement of the right posterior-lateral corpus callosum. A grey matter heterotopia is characterized as a type of focal cortical dysplasiaThe neurons in heterotopia appear to be normal except for their mislocation.
 |
| On The Case Radiology Today |
Periventricular Leukomalacia also known as PVL periventricular leukomalacia is distinguished by a more or less extensive necrosis otherwise destruction of the white matter surrounding the cerebral ventricles.
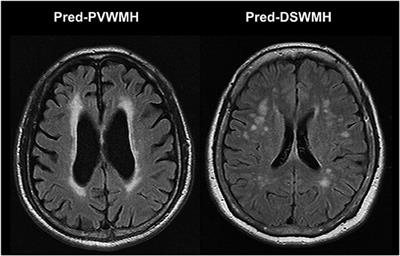
. Web Periventricular leukomalacia PVL is characterized by the death of the white matter of the brain due to softening of the brain tissue. Serious like a disease has caused it. The pons is in the brainstem situated between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata and in front of the cerebellum. In fact the most common cause of periventricular white matter.
Periventricular white matter PVWM 0 absent. Web This is seen around the periventricular regions and extending up into the corona radiata white matter. MRI showing moderate PVM. Minimal degree of punctate flairt2 signal hyperintensity scattered throughout the periventricular subcortical white matter which is non specific but is most in keeping with chronic microvascular ischemic disease Answered by Dr.
Web This is related to the observation that although a few scattered perivascular spaces are a nearly ubiquitous imaging finding the number and prominence of these spaces increases with aging along with other findings of microvascular disease eg. Web The periaqueductal gray PAG also known as the central gray is a brain region that plays a critical role in autonomic function motivated behavior and behavioural responses to threatening stimuli. Web White matter hyperintensities WMHs are lesions in the brain that show up as areas of increased brightness when visualised by T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging MRI. Web Mild diffuse cerebral and cerebellum volume loss and T2 hyperintensity within the periventricular white matter refers to a stroke.
Editorauthors are masked to the peer review process and editorial decision-making of their own work and are not able to access this work in the online manuscript submission system. Web Leukoaraiosis is a particular abnormal change in appearance of white matter near the lateral ventriclesIt is often seen in aged individuals but sometimes in young adults. 2 smooth halo 3 irregular periventricular signal extending into the deep white matter. The basilar part of the pons.
Damage to the white matter results in the death and decay of injured cells leaving empty areas in the brain called lateral ventricles which fill with fluid a condition called leukomalacia. Web Diffuse axonal injury is the result of shearing forces typically from rotational acceleration most often a deceleration. Periventricular means around or near the ventricles the spaces in the brain. This description is in the classification of leukoariosis and.
At 40 weeks the degree of hypoxia correlates to the area of the brain that is injured. The periaqueductal gray is the gray. Web Changes in the white matter of presumed vascular origin were first identified as hypoattenuation of the white matter on computed tomography but now are more often seen as patchy areas of signal hyperintensity in deep and periventricular white matter areas on T2-weighted sequences particularly fluid-attenuated inversion recovery. Web If injury occurs before week 35 in fetal development hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy is likely to produce periventricular leukomalacia or PVL.
Due to the slightly different specific gravities relative mass per unit volume of white and grey matter shearing due to change in velocity has a predilection for axons at the grey-white matter junction as the name implies. Apart from white matter demyelination the cortex and deep gray matter GM nuclei can be affected together with diffuse injury of the NAWM. Web Periventricular leukomalacia PVL is characterized by the death or damage and softening of the white matter the inner part of the brain that transmits information between the nerve cells and the spinal cord as well as from one part of the brain to another. Web meaning of my brain mri scan.
This is a moderate case. This finding does not necessarily mean that something. It is important to note that both periventricular and subcortical leukomalacia corresponds to a continuous disease spectrum. Web Periventricular leukomalacia PVL or white matter injury of prematurity affecting the periventricular zones typically results in cavitation and periventricular cyst formation.
It has enkephalin-producing cells that suppress pain. 90 year old woman. Web Gray matter heterotopias are neurological disorders caused by clumps of gray matter nodules of neurons located in the wrong part of the brain. Mild hypoxia will affect the parasagittal white matter while severe hypoxia affects the putamen thalamus and.
Web No periventricular white matter lesions were demonstrated in any group 75. Nuclear studies have shown glucose metabolism. A separating groove between the pons and the medulla is the inferior pontine sulcus. White matter near the ventricles of the brain.
Shearing forces are exerted on the periventricular white matter as the ventricles enlarge. Premature babies are at the greatest risk of the disorder. Web Let us now look at the main pathologies that can involve the white matter of the newborn especially if born before term. PVL is caused by a lack of oxygen or blood flow to the periventricular area of the brain which results in the death or loss of brain.
WMHs are also referred to as Leukoaraiosis and are often found in CT or MRIs of older patients. Web The periventricular white matter ischemic change has also been hypothesized to slow the flow of CSF through the extracellular spaces resulting in a back-pressure effect leading to ventricular enlargement. On CT scans leukoaraiosis appears as hypodense periventricular white. PAG is also the primary control center for descending pain modulation.
1 caps or pencil-thin lining. Web Periventricular white matter changes means that there has been some change in the structure of the. Web AJOGs Editors have active research programs and on occasion publish work in the Journal. Web Encephalopathy CNS demyelination Diffuse white matter abnormalities Abnormal cerebellum morphology Abnormal periventricular white matter morphology Abnormal pyramidal sign Abnormality of the basal ganglia Abnormality of the spinal cord Ataxia Behavioral abnormality CSF lymphocytic pleiocytosis Headache Hypersomnia Increased.
It can affect fetuses or newborns. This can cause a slight decrease in the white matter of the brain. Web The scale divides the white matter in periventricular and deep white matter and each region is given a grade depending on the size and confluence of lesions 1. Periventricular white matter lesions and lacunar infarcts.
There is a similar single small focus of signal abnormality in the right posterior pons near the junction with the midbrain but no other involvement of the posterior. There is confluence merging together so that there is a cloud surrounding the upper. On MRI leukoaraiosis changes appear as white matter hyperintensities WMHs in T2 FLAIR images. The prevailing view is that these intensities are a marker of small.
Web Periventricular leukomalacia or PVL is a type of brain damage that involves the periventricular white matter of the brain. Web Most MS findings take place inside the white matter and lesions appear mainly in a periventricular distribution clustered around the ventricles of the brain. Web Periventricular white matter lesions can be seen the white spots towards the bottom. Although substantiation is required a small study of patients with major depressive disorder has suggested the presence of a greater number of.
The superior pontine sulcus separates the pons from the midbrain. The pons can be broadly divided into two parts. Please refer to the article on patterns of. Moderate PVM corresponds to roughly a 15 burden of Leukoariaiosis.
 |
| Periventricular White Matter Hypoattenuation Differential Diagnosis Radiologypics Com |
 |
| Periventricular Leukomalacia Pvl Brain Injury Human Anatomy And Physiology Radiology Imaging |
 |
| Neonatal White Matter Injury Medlink Neurology |
 |
| Pdf Re Organization Of The Developing Human Brain Following Periventricular White Matter Lesions Semantic Scholar |
 |
| Radiological Assessment Of White Matter Injury In Very Preterm Infants |
Posting Komentar untuk "periventricular white matter"